As per Microsoft, Windows Autopilot is a collection of technologies used to set up and pre-configure new devices and prepare them for productive use. You can also use Windows Autopilot to reset, repurpose, and recover devices. This solution enables an IT department to achieve the above with little to no infrastructure to manage, and by following a process that is simple and easy to manage.
In this post, we will discuss device provisioning using Windows 10 Autopilot for Azure Active Directory / Entra ID joined devices.
- Configure Azure Active Directory Automatic Enrollment
- Configure Azure Active Directory custom branding (Optional)
- Create a device group for Windows Autopilot
- Create Windows Autopilot Deployment Profile
- Configure Enrollment Status Page
- Manually Register the Device with Windows Autopilot
- Reset the VM to factory settings
- Out of Box Experience (OOBE)
- Related Posts:
Configure Azure Active Directory Automatic Enrollment
Automatic enrollment lets the user automatically enroll their Windows devices in Microsoft Intune. When the device joins Azure AD, it automatically gets enrolled in Microsoft Intune.
Follow the below steps to configure Automatic MDM enrollment from the Azure portal.
- Sign in to the Azure portal, and select Azure Active Directory > Mobility (MDM and MAM) > Microsoft Intune.
- Configure MDM user scope. If you select Some then you need to select an Azure AD Group.
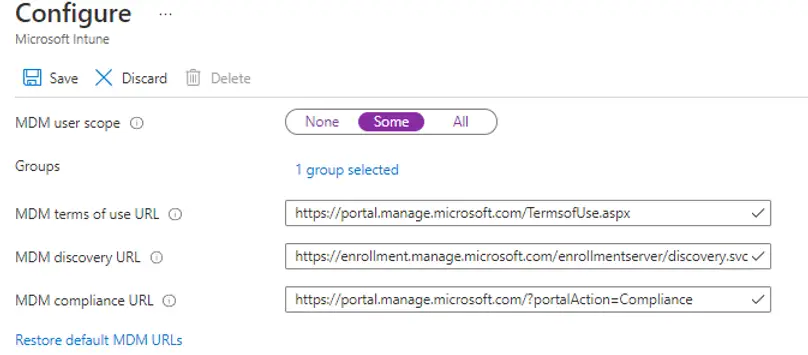
Note: MDM user scope must be set to an Azure AD group that contains user objects.
Configure Azure Active Directory custom branding (Optional)
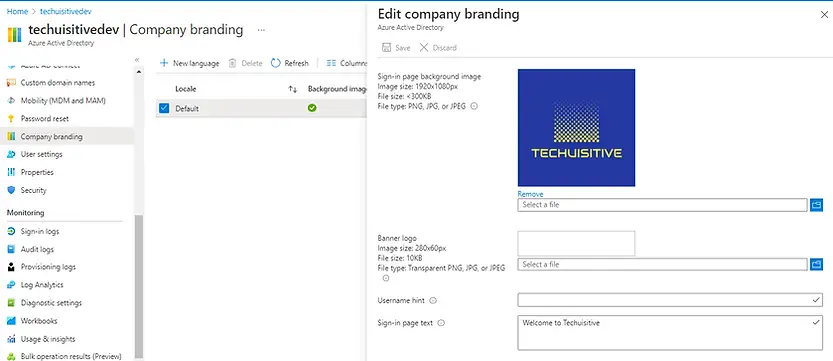
The Azure Active Directory custom branding page allows you to configure an organization-specific login page. You can add company branding to your sign-in page in Azure AD. You can configure these settings from Azure portal > Azure AD > Company branding.
Create a device group for Windows Autopilot
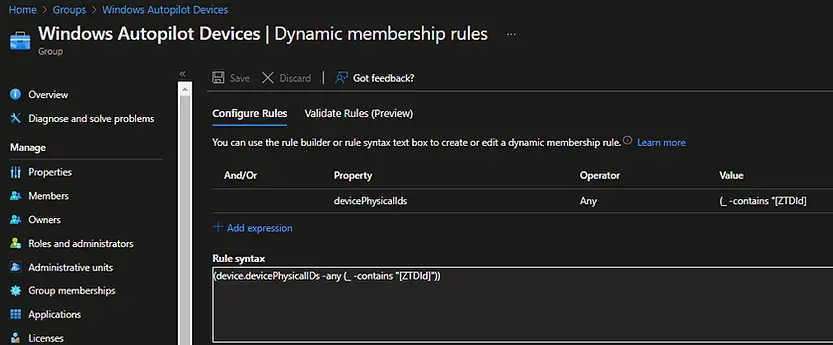
A device group is required to assign an Intune Autopilot Deployment Profile. We will create a group with dynamic membership using Autopilot device attributes (ZTDId). This will reduce the manual efforts of adding each device to the group as the device automatically becomes a member of the group when the hardware hash is imported into Windows Autopilot.
To create a group that includes all of your Autopilot devices, use the below expression in the dynamic membership rule:
(device.devicePhysicalIDs -any (_ -contains “[ZTDId]”))
Create Windows Autopilot Deployment Profile
Autopilot deployment profiles are used to configure the Autopilot devices. A Windows Autopilot Deployment Profile needs to be assigned to devices to enable Windows autopilot for them. Follow the below steps to create an Autopilot deployment profile.
In the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, choose Devices > Windows > Windows enrollment > Deployment Profiles
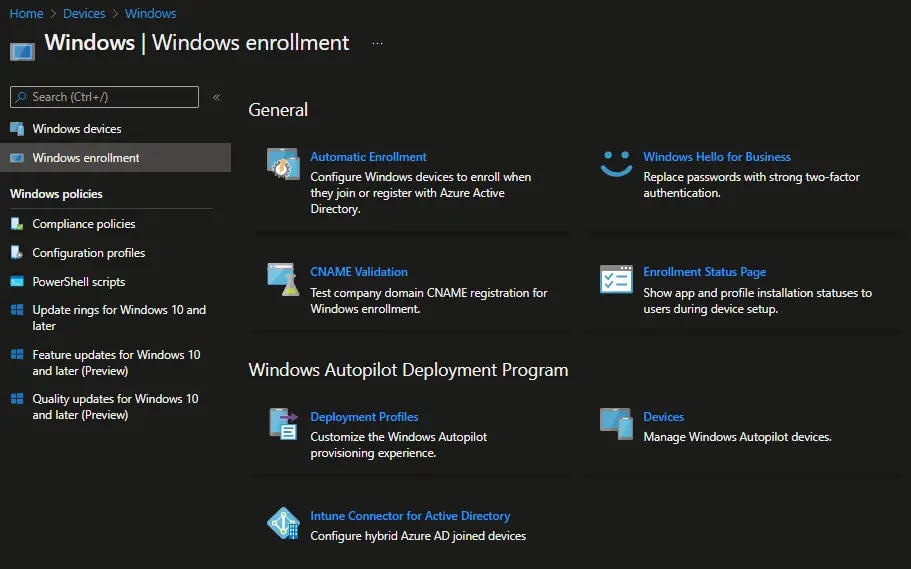
Click on Create Profile > Windows PC
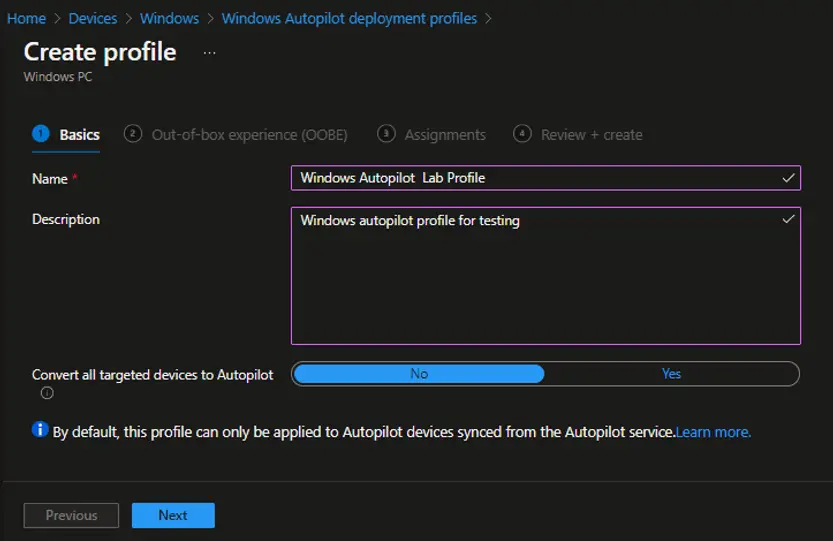
On the Basics page, type a Name and optional Description. Click on Next.
On the Out-of-Box Experience (OOBE) page, we will go ahead with all default settings.
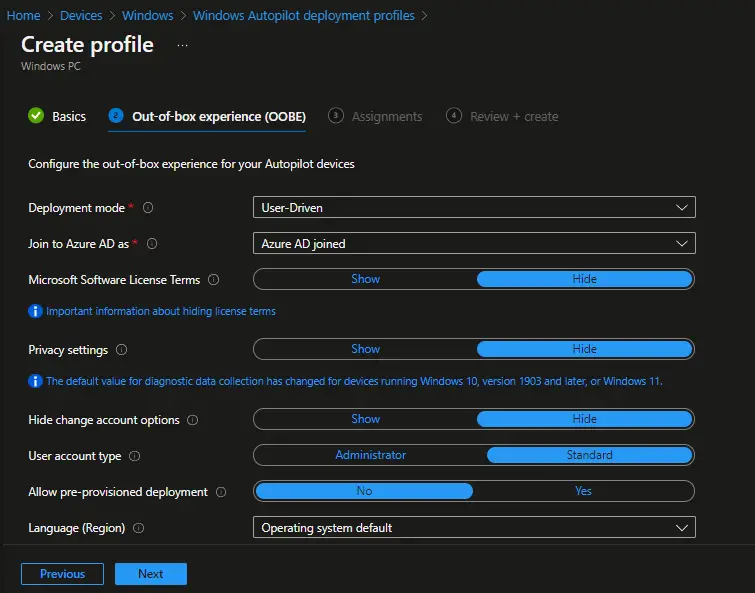
Settings:
- Deployment Mode: User Driven
Devices with this profile require users to enroll the device using their Microsoft Entra ID (Formerly Azure Active Directory) credential.
- Join to Azure AD: Azure AD joined
- Microsoft Software License Terms: Hide
- Privacy Settings: Hide
- Hide change account options: Hide
- User Account type: Standard
- Allow White Glove OOBE: No
- Language (Region): Operating System default
- Automatically Configure keyboard: Yes
- Apply device name template: Yes
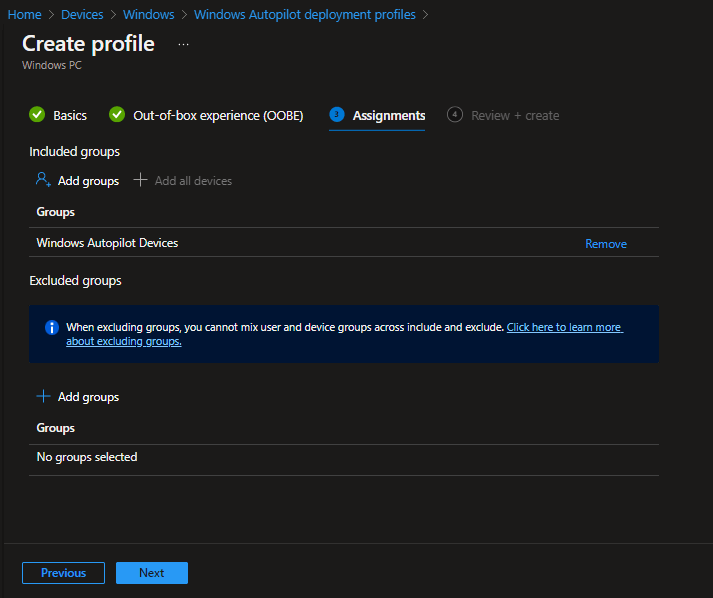
On the Assignment page, add the AAD group you created for Windows Autopilot Devices and click on Next.
On the Review + Create page, review the details and click on Create button.
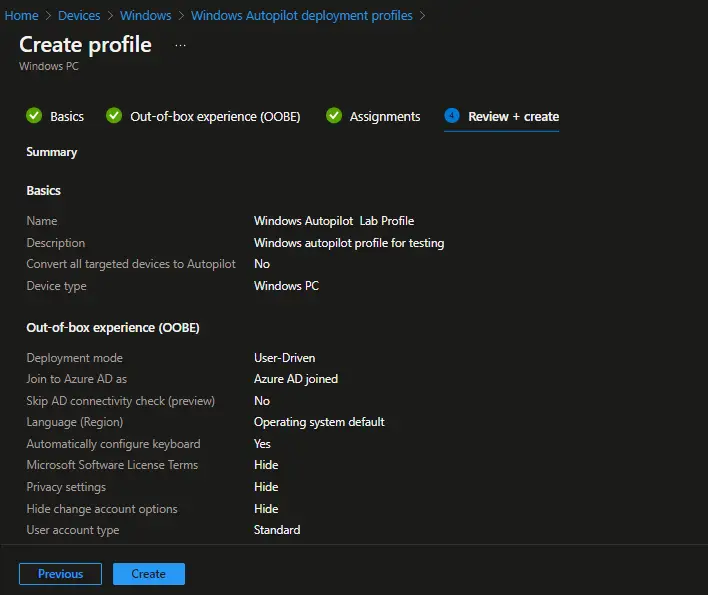
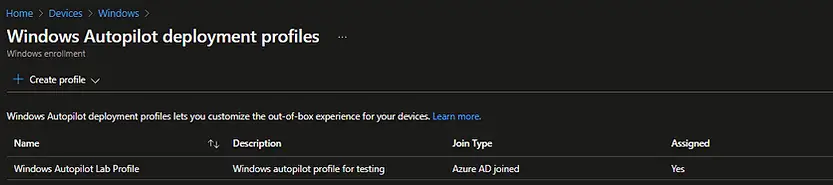
The Autopilot deployment profile is now created and you can see the same from Devices > Windows Enrollment > Windows Autopilot Deployment Profile.
Configure Enrollment Status Page
The Enrollment Status Page (ESP) shows the progress of device provisioning when a new device is enrolled in Intune or a new user signs in to the device. You can show ESP during the default out-of-box experience (OOBE) for Azure AD join, Windows Autopilot scenarios, or when new users sign into the device for the first time.
Check out this post for the step-by-step guide to configuring the Enrollment Status Page.
Manually Register the Device with Windows Autopilot
We have configured all required settings in Intune to support Windows autopilot scenarios. Now, we need to manually register the device to Windows Autopilot to go ahead with our testing.
The manual hardware hash registration process is primarily for testing purposes. An organization should opt for OEMs or CSP partners for Windows Autopilot registration. An OEM or other device provider uses the registration authorization process to perform device registration on your behalf.
All major hardware vendors such as Dell, HP, and Lenovo support the Windows Autopilot OEM partner program. You can check out this article to invite Dell for Windows autopilot OEM partner.
Follow the below steps to register a device to Windows Autopilot.
- Install Windows 10 on a test device or VM. We will use the same device for Autopilot deployment.
- Download the PowerShell script (Get-WindowsAutoPilotInfo.ps1) from the PowerShell gallery to get a device’s hardware hash and serial number. The serial number is useful for quickly seeing which device the hardware hash belongs to.
- Run the Powershell script on the test device that you prepared for Windows Autopilot deployment testing.
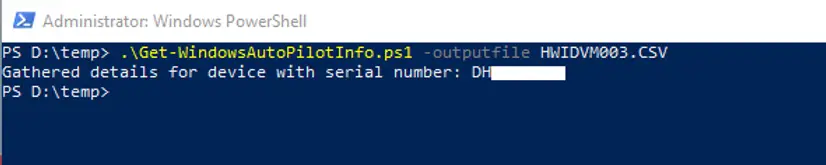
Once we done with capturing hardware hash in CSV file the same need to be uploaded to Windows Autopilot. We will use Microsoft Intune to import the device to Windows Autopilot.
In the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center, choose Devices > Windows > Windows enrollment and select Devices in Windows Autopilot Deployment Program section
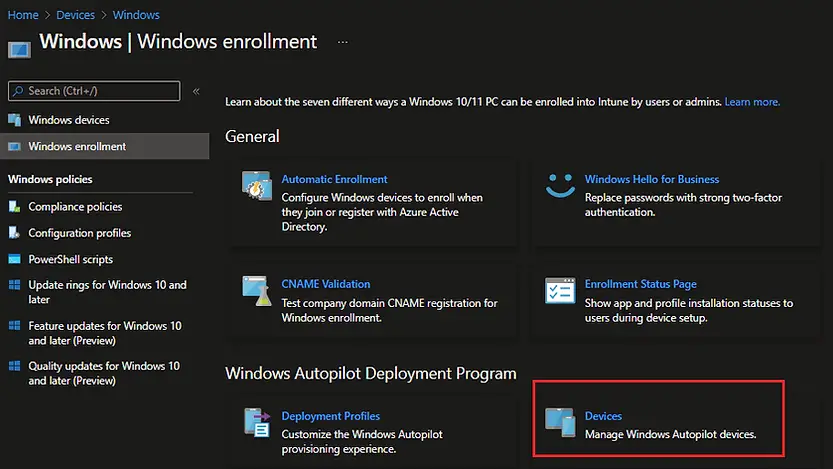
On the next screen, click on Import
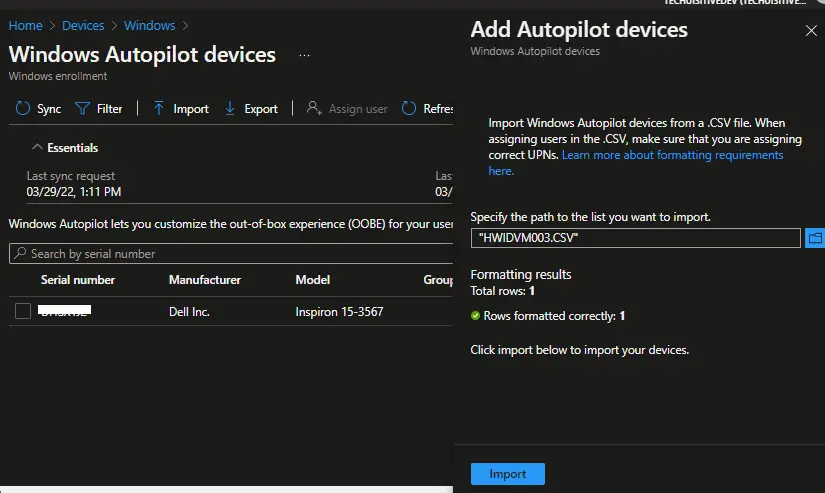
On the Add Autopilot devices screen, click on the Browse button and select the hardware hash CSV file. Click on Import.
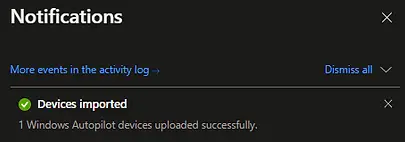
You can see the status of imports in the Notification area.
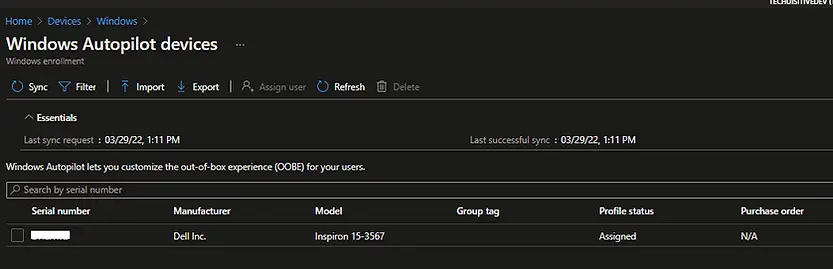
If Import was successful then you will see the device details in Windows Autopilot Devices page.

Reset the VM to factory settings
Now we need to reset the Windows 10 VM to factory settings. This will force the device to go to the Windows setup OOBE stage. The Windows Autopilot profile downloads automatically from Windows Autopilot Services at this stage. However, before resetting the device, you must ensure that the device is connected to the network and the Internet is accessible.
Perform the below steps to reset your Windows OS to factory settings.
- From the Start Menu, select Settings
- In the Windows Settings window select Update & Security
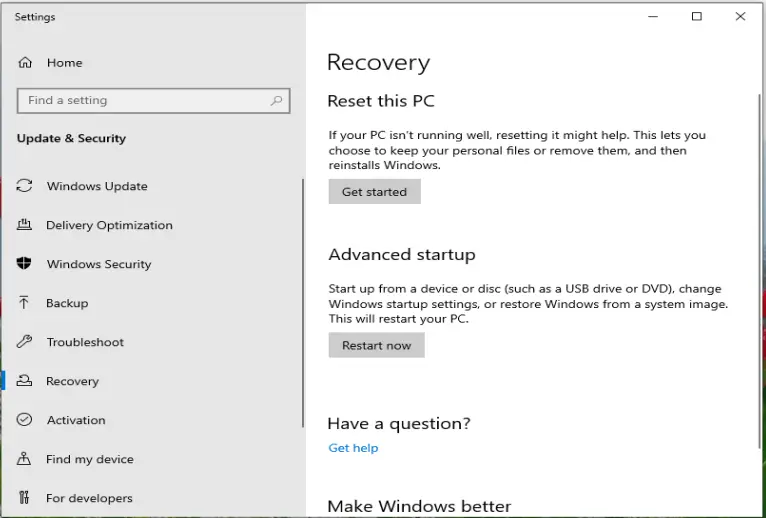
- In the Windows Update window select Recovery from the left pane
You will now see the Recovery page. Click on Get Started under Reset this PC to begin the reset process.
Windows 10 – Reset
On the Choose an option page, select Remove Everything.
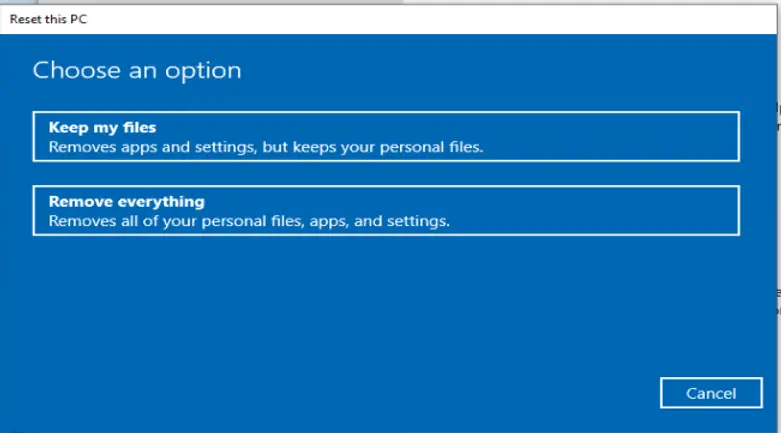
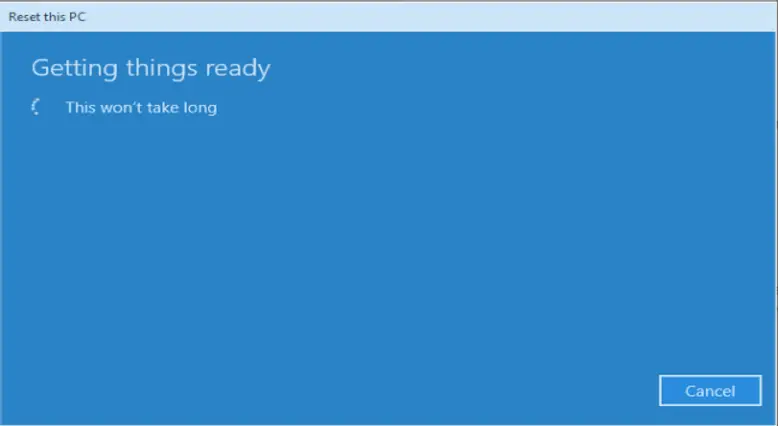
You will see the “Getting things ready” page. The machine reboots once the reset process completes and it takes you to the Windows setup OOBE page after reboot.
Out of Box Experience (OOBE)
We have reset our test VM in the previous steps. Once the reset process is completed, it will go to OOBE screen. The first few screens will have the following details. The end user will go through the same experience.
Network connection: When you reset a Windows 10 OS, the network details such as WIFI connection and password are saved and automatically restored. Hence, you may not see this screen.
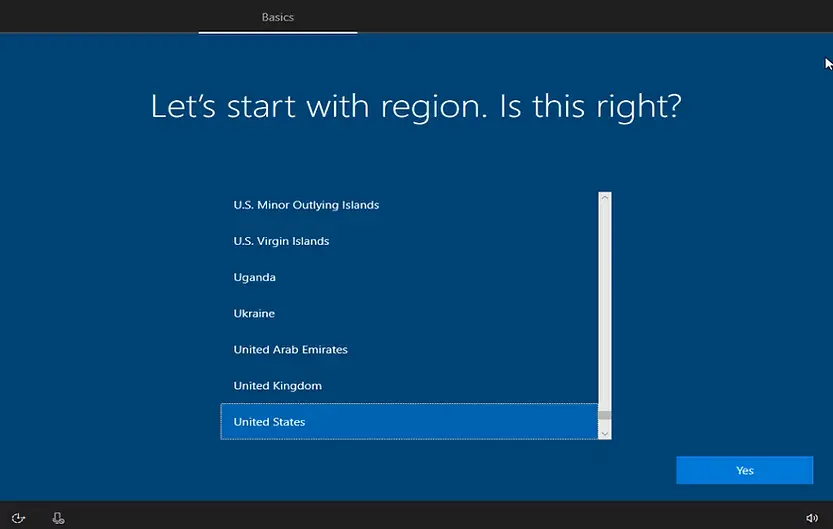
Region settings: Select the region
Keyboard layout: Select the Keyboard layout
Additional keyboard layout: This screen will allow you to add additional keyboard layout
license agreement: Acknowledge the license agreement
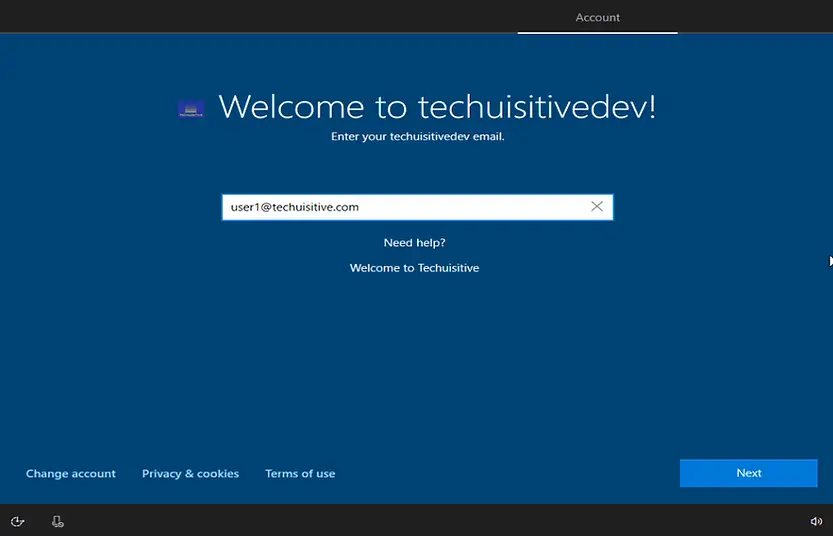
The next screen will be for user login. If you don’t see your company branding and tenant details here then your device has not been identified as a Windows Autopilot device.
The user should log in with their corporate ID and password. Enter your company corporate ID and click on Next.
You will be prompted for the password on the next screen. Enter the password and click on Next.
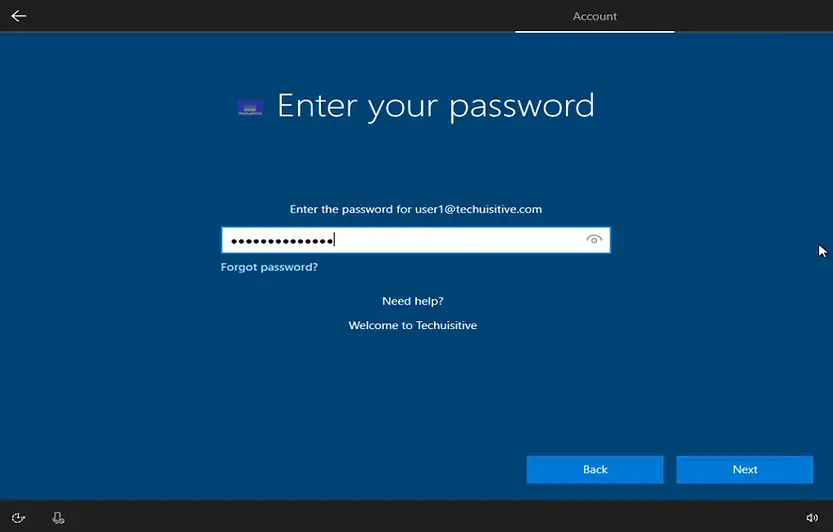
The Enrollment Status Page (ESP) will be displayed on the next screen.
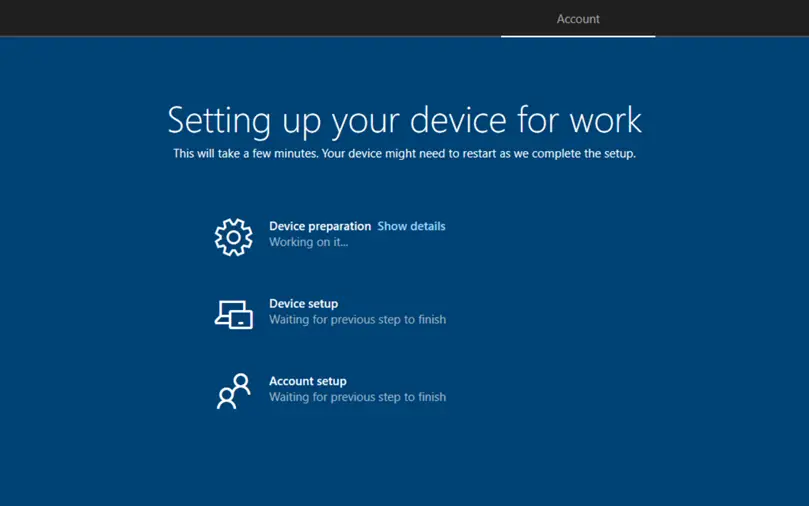
The following stages will be part of an Enrollment Status page.
Device Preparation:
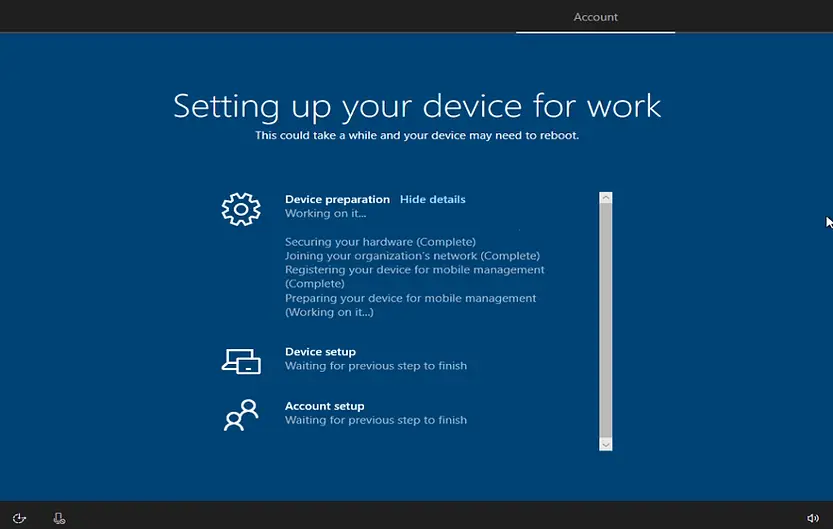
The following actions are included in the Device preparation stage.
- Securing your hardware
- Joining your organization’s network
- Registering your Device for Mobile Device Management
- Preparing your device for mobile management
Device Setup:
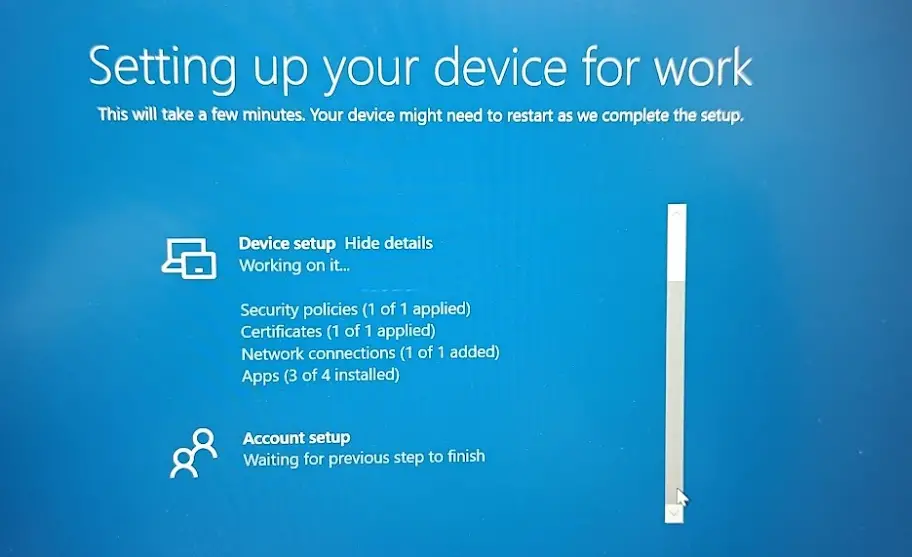
During the device setup phase in the Enrollment Status Page (ESP), Autopilot ensures essential configurations are applied before the user can access the system. The device receives security policies and installs required apps via Intune.
The Device setup stage includes the following steps.
- Security Policies
- Certificate
- Network Connections
- Apps
Account Setup:
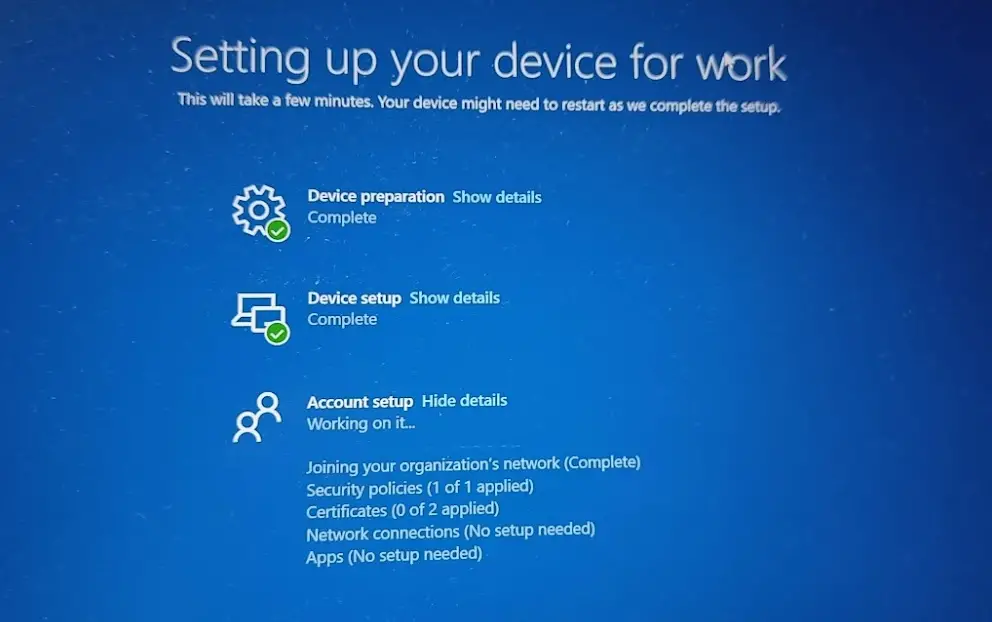
The Account setup is the last stage of the Enrollment Status Page. During the account setup phase, the device is joined to Microsoft Entra ID or Azure AD, compliance policies are enforced, and required apps are installed via Intune.
The following actions are associated with this stage.
- Joining your organization’s network
- Security policies
- Certificates
- Network connections
- Apps
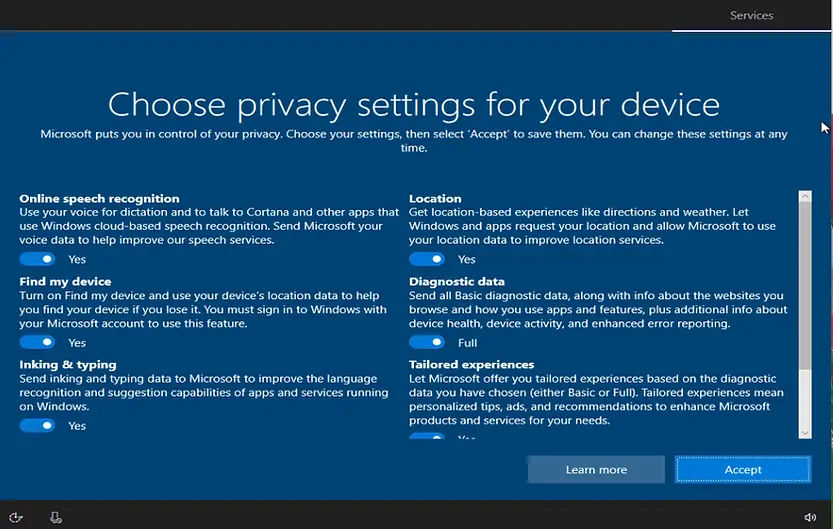
The next screen will be Privacy settings. Toggle the settings on or off as per your requirements and click on Accept.
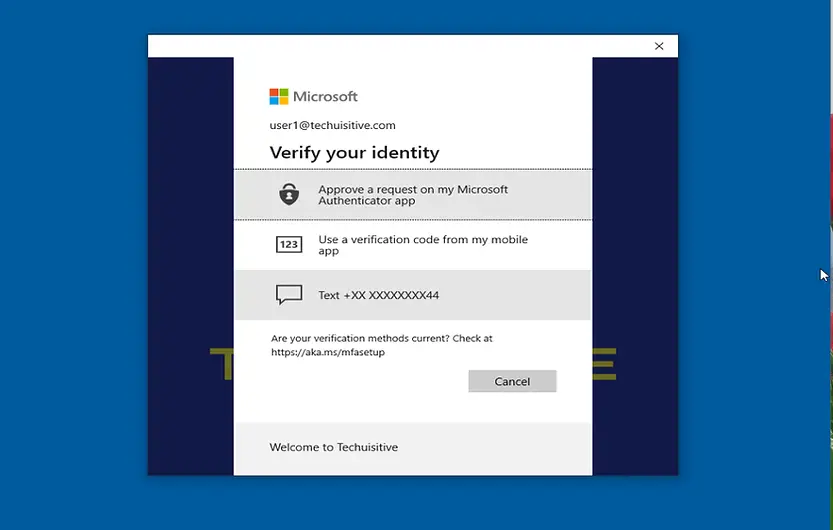
Once enrollment configurations are finished, the user will get a prompt for additional authentication if Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is enabled.
Your device is now ready to use.
Related Posts:
- Windows Autopilot Device Preparation – Step-by-Step Guide
- Windows 10 Autopilot Deployment Guide | Intune
- Intune – Configure Enrollment Status Page (ESP)
- Intune – Windows 10 MDM- Basic troubleshooting
- Bulk enrollment of Windows 10/ 11 Device to Intune using Provisioning Package
- Enroll Windows 11 Device to Intune through Azure AD Join method
- Windows 11 enrollment with Provisioning package failed with error code 0x800700b7
- How to Obtain Hardware Hash for Manually Registering Devices with Windows Autopilot
- Dynamic Group Based on Enrollment Profile in Intune.
Subscribe to Techuisitive Newsletter
Be the first to know about our new blog posts. Get our newsletters directly in your inbox and stay up to date about Modern Desktop Management technologies & news.